It’s may be a bit overused, but I’m going to start this essay with a Kundera quote from The Book of Laughter and Forgetting.
“In February 1948, the Communist leader Klement Gottwald stepped out on to the balcony of a Baroque palace in Prague to harangue hundreds of thousands of citizens massed in Old Town Square. That was the great turning point in the history of Bohemia. A fateful moment of the kind that occurs only once or twice a millennium.
“Gottwald was flanked by his comrades, with Clementis standing close by him. It was snowing and cold, and Gottwald was bareheaded. Bursting with solicitude, Clementis took off his fur hat and set it on Gottwald’s head.
“The propaganda section made hundreds of thousands of copies of the photograph taken on the balcony where Gottwald, in a fur hat and surrounded by his comrades, spoke to the people. On that balcony the history of Communist Bohemia began. Every child knew that photograph, from seeing it on posters and in schoolbooks and museums.
“Four years later, Clementis was charged with treason and hanged. The propaganda section immediately made him vanish from history, and of course, from all photographs. Ever since, Gottwald has been alone on that balcony. Where Clementis stood, there is only the bare palace wall. Nothing remains of Clementis but the fur hat on Gottwald’s head.”
There are numerous examples of removing someone from history, mostly from national leaders who didn’t need subtlety in their actions.
Some of the most obvious examples come from authoritarians and apart from Gottwald, include Stalin’s historical removal of Leon Trotsky and Nikolai Yezhov, or Mao’s removal of Bo Gu. But how else do we remove people from history? Does the inability to ever truly erase something online change this?
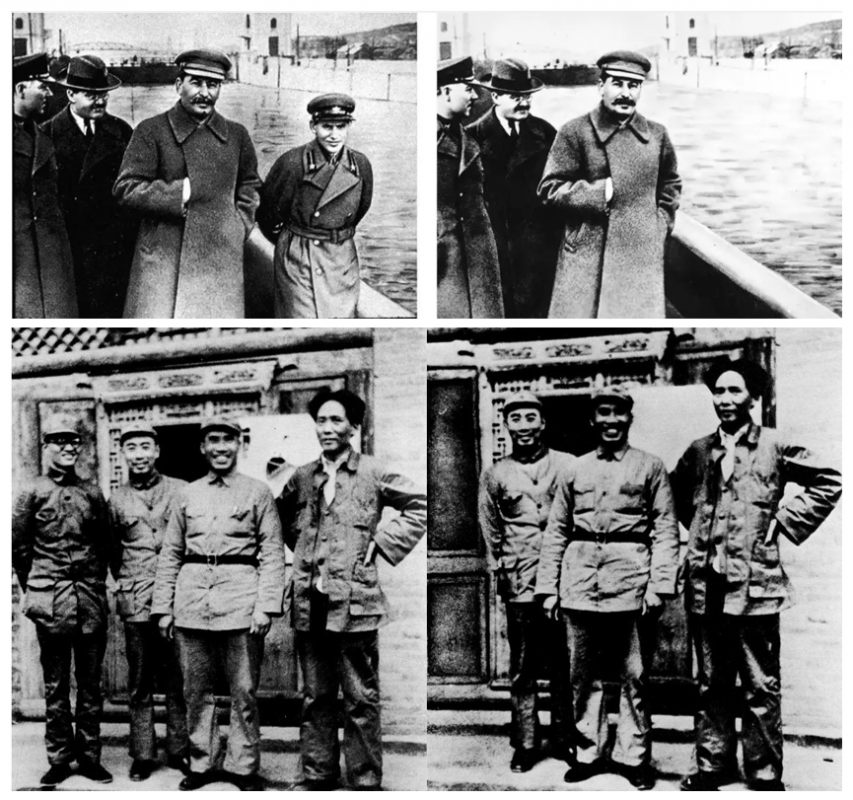
Let’s look at ways we choose to eliminate history and when we do it. Continue reading “A Question of Timing (Erasing History)”